# All Libraries required for this lab are listed below. Already installed so this code block is commented out
pip install pandas==1.3.4
pip install scikit-learn==1.0.2
pip install numpy==1.21.6Evaluation of LR Model - MPG
Objectives
We will use car dataset to build/Split/Train/Test a linear regression model that will predict the mileage of a car
Here is a list of Tasks we’ll be doing:
- Use Pandas to load data sets.
- Identify the target and features.
- Split the dataset into training and testing files
- Use Linear Regression to build/train a model to predict car mileage.
- Test the model and create predictions.
- Use metrics to evaluate the model.
Jupyter notebook is found at: Building_and_training_a_model_using_Linear_Regression_1.ipynb
Setup
We will be using the following libraries:
pandasfor managing the data.sklearnfor machine learning and machine-learning-pipeline related functions.
Install Libraries
Suppress Warnings
To suppress warnings generated by our code, we’ll use this code block
# To suppress warnings generated by the code
def warn(*args, **kwargs):
pass
import warnings
warnings.warn = warn
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')Import Libraries
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
#import functions for train test split
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# import functions for metrics
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from math import sqrtData - Task 1
- Modified version of car mileage dataset. Available at https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/auto+mpg
- Modified version of diamonds dataset. Available at https://www.openml.org/search?type=data&sort=runs&id=42225&status=active
Load
# the data set is available at the url below.
URL = "https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/IBM-BD0231EN-SkillsNetwork/datasets/mpg.csv"
# Load data with: read_csv function into a pandas dataframe.
df = pd.read_csv(URL)
# Review the data
# df.sample(5)| MPG | Cylinders | Engine Disp | Horsepower | Weight | Accelerate | Year | Origin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 | 27.2 | 4 | 141.0 | 71 | 3190 | 24.8 | 79 | European |
| 126 | 14.0 | 8 | 304.0 | 150 | 4257 | 15.5 | 74 | American |
| 150 | 20.0 | 6 | 232.0 | 100 | 2914 | 16.0 | 75 | American |
| 224 | 25.5 | 4 | 140.0 | 89 | 2755 | 15.8 | 77 | American |
| 175 | 22.0 | 4 | 121.0 | 98 | 2945 | 14.5 | 75 | European |
Count Rows & Columns
df.shape(392, 8)Scatter Plot Data
- First we’ll plot HP vs MPG
df.plot.scatter(x = "Horsepower", y = "MPG")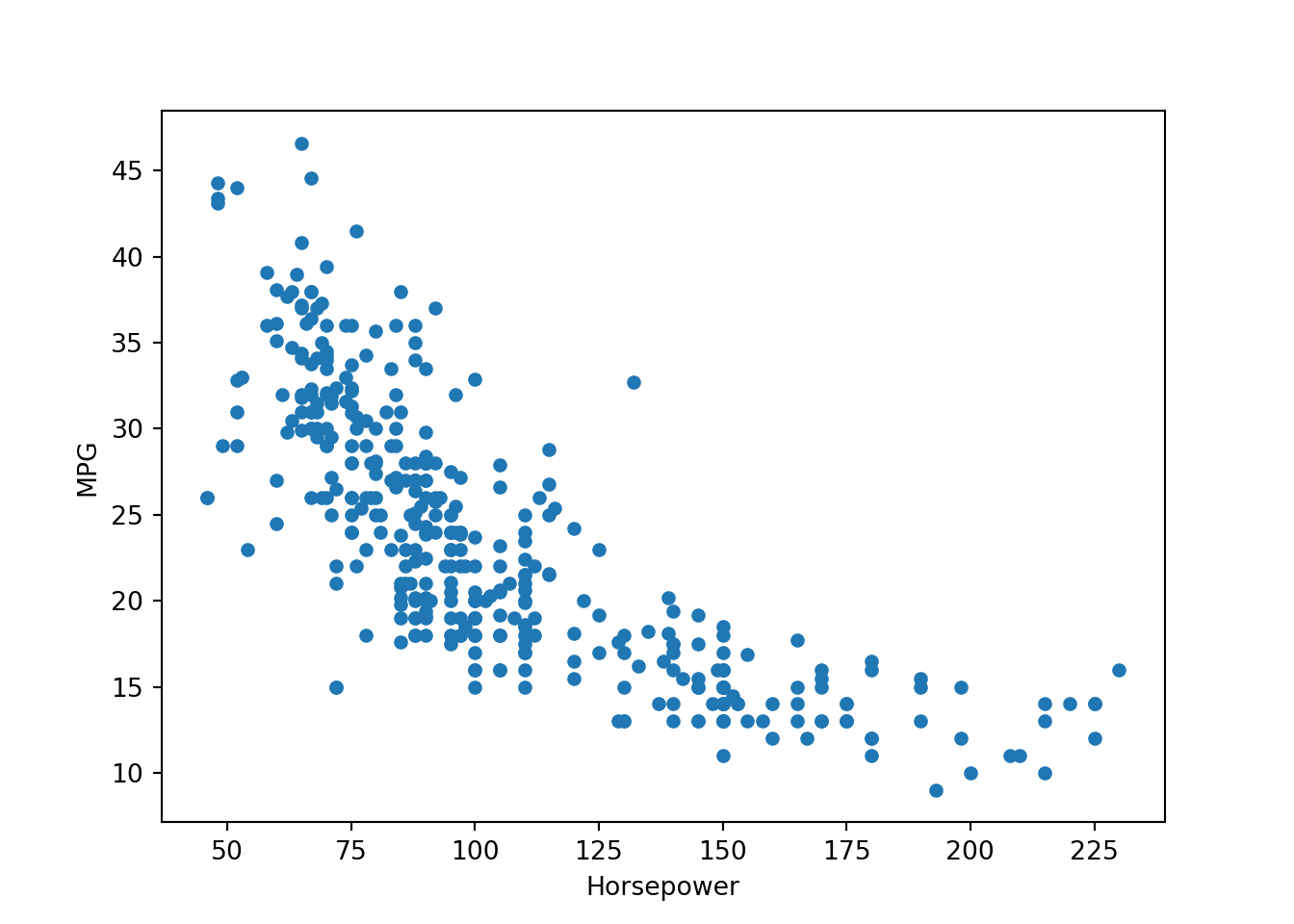
- Now let’s plot Weight vs MPG
df.plot.scatter(x = "Weight", y = "MPG")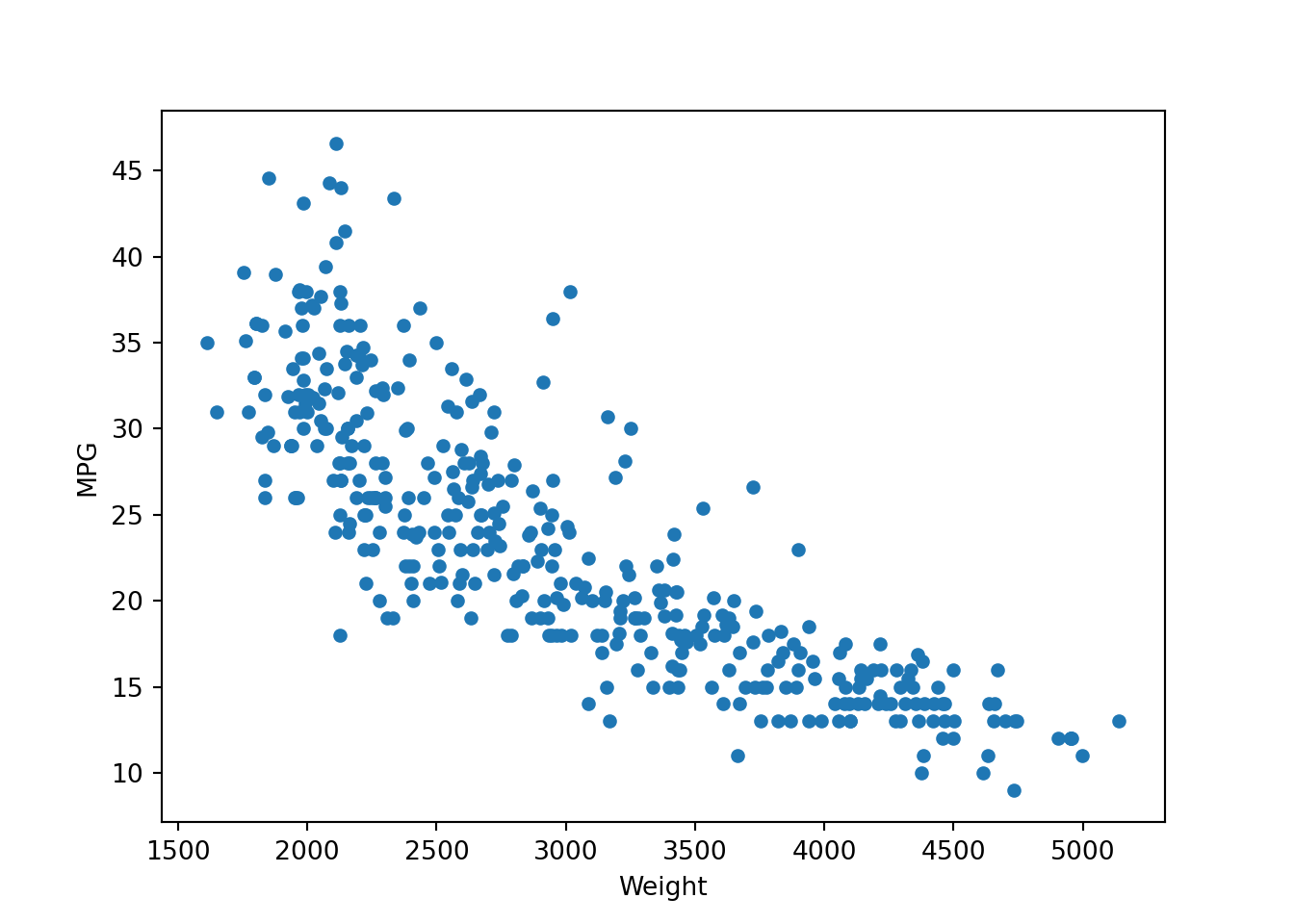
Define Targets/Features - Task 2
Target
In LR models we aim to predict the Target value given Input/Data.
So, in this example we are trying to find the MPG which is the Target Column in our table or y axis
Y = df['MPG']Features
The feature(s) is/are the data columns (or x axis), we will provide our model with as input from which we want it to predict the Target Value/Column
In our example let’s provide the model with these Features, and see how accurate it will be in predicting the MPG
- Horsepower
- Weight
X = df[['Horsepower', 'Weight']]Split Dataset - Task 3
- We now split the data at 70/30 ratio, 70 training, 30 testing
- The random_state variable controls the shuffling applied to the data before applying the split.
- Pass the same integer for reproducible output across multiple function calls
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.30, random_state=42)Build/Train LR Model - Task 4
Define LR Model
lr = LinearRegression()Train/Fit LR Model
Let’s train it. The response will be
- Remember the formula was:
lr.fit( features,target) - LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=None, normalize=False)
lr.fit(X_train, Y_train)LinearRegression()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LinearRegression()
Test/Evaluate Model - Task 5
Now that the model has been trained on the data/features provided above, let’s test it
Score
The higher the better in LR Models
#Higher the score, better the model. Remember Y is the target MPG
lr.score(X_test, Y_test)0.7691968626070728Predict
In order to calculate the score metrics we need two values:
- The original MPG which are the MPG from the test data set and we’ll compare to the predicted values
- The predicted MPG which are the results of the model
original_values = Y_test
predicted_values = lr.predict(X_test)Evaluation Metrics - Task 6
R squared
Higher the value the better the model
# Higher the value the better the model
r2_score(original_values, predicted_values)0.7691968626070728Mean Squared Error - MSE
The lower the value the better the model
mean_squared_error(original_values, predicted_values)12.21274893832399Root MSE - RMSE
The lower the value the better the model
sqrt(mean_squared_error(original_values, predicted_values))3.4946743679953918Mean Absolute Error
The lower the value the better the model
mean_absolute_error(original_values, predicted_values)2.8530678815092534